
August 9 2023
4 min read
May
Decomposition refers to breaking down the project deliverables into smaller, more detailed, and manageable work packages. This prepares a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) that ensures project deliverables are clearly defined and that the work involved in completing each deliverable is fully understood.
By breaking the work down into smaller components, it becomes easier to estimate the time, cost, and resources required for each work package, as well as to identify any potential risks, dependencies, or constraints that may impact the project.
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a hierarchical decomposition of the project deliverables into smaller, more manageable components.
In this article, we will explore:
What is a WBS?
Role of WBS in project management
How to design an effective WBS?
Different approaches to organizing a WBS
The WBS is a hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables. It is typically represented as a tree-like structure, where the primary deliverable is at the top, and the subsequent levels represent the breakdown of the deliverable into more detailed and manageable components.
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a fundamental project management technique for defining and organizing project work, using a hierarchical tree structure – thus providing a structured vision of what will be delivered.
WBS details the interim and team-level deliverables that must be produced to accomplish the project scope. It covers the product and project-level deliverables. WBS serves as a foundation for planning (scheduling and budgeting primarily)
The beauty of the WBS is that the entire project can be thought out in advance.
Following are some of the reasons for creating a WBS:
Defining project scope - Accurately and precisely define and organize the scope, preventing work from slipping through the cracks.
Provides a basis for estimating (time and cost) - A WBS breaks down work into small chunks which can be accurately estimated for time and cost. These work package level time and cost can be rolled up to higher levels and finally to the project level to get a time and cost estimate for the project.
Facilitate Work/Resource allocation - Once the work is broken into small manageable components, these can be assigned to individual team members.
Helps monitor and control the project - The WBS provides a basis for monitoring and controlling project progress by allowing project managers to track progress at each level of the WBS. Monitoring tends to be more effective when performed at a micro level (work package).
Ensure team Buy-in - Provides the project team with an understanding of where their pieces fit into the overall project. It is recommended that the project manager involves the team in WBS creation.
Support Risk Management - Can be used as a prompt list to identify risks in the project, resulting in an exhaustive identification of risks.
Facilitating communication - The WBS can foster communication among project stakeholders by providing a common understanding of the project scope, deliverables, and tasks. The WBS can also ensure everyone is on the same page regarding the project’s objectives and requirements.
Support change management - The WBS can be used to support change management by allowing project managers to identify the impact of changes to the project scope, deliverables, or tasks
Support resource management - The WBS can support resource management by identifying the resources required for each work package. This allows project managers to allocate resources effectively.
100% Rule
This means “All the work and only the work.” The total of child components should equal the parent component – for every level of decomposition. Must include work such as Project Management, Quality, Integration, etc., and not only development.
Outcomes and not actions
Attempting to define actions now may make it challenging to adhere to the 100% rule. This also ensures the WBS is not overly prescriptive, allowing creativity on the part of the team to decide on the way to produce deliverables.
Mutually Exclusive components
No overlapping elements. This can result in duplication of work, thus land up in over-estimating the project, ambiguity in responsibilities, etc.
The lowest level WBS elements are known as Work Packages - the smallest deliverables in the project that cannot be broken down any further.
An adequate level of granularity is achieved when it is impossible to break down into outcomes. Some considerations when deciding at what level to stop include - is it small enough to estimate accurately? Will monitoring be effective at this level?
The number of levels in the WBS would vary from project to project and is influenced by factors such as the size and complexity of the project, the experience level of the team, etc.
40-Hour rule - Effort required to produce a Work Package should be within 40 hours or one week.
80-Hour rule - The effort required to produce a Work Package should be within 80 hours or 2 weeks.
4% rule - As per this rule, a WBS has been adequately decomposed if the size of a Work Package is no more than 4% of the overall project size.
Although the WBS is a deliverable-oriented breakdown, there are many other types (approaches) of WBS in practice. Some commonly adopted ones include.
Verb Oriented – Arranged in terms of actions to produce deliverables (like Design, Develop, test, etc.)
Noun Oriented – Broken down in terms of the components that make up the ultimate project deliverable. These are the parts of a deliverable, at times called a “Product Breakdown Structure (like Engine, Chassis, Electrical Assembly, etc.)
Time-phased – Projects are often broken down into phases. In this, a ‘rolling wave’ approach is used where only the near term is planned in detail.
Further, there are many other approaches used by project managers cost-oriented (breaking down into cost elements), location-oriented (suitable for projects with multiple locations), resource-oriented (into types of resources required), system-oriented (into systems or sub-systems)
A verb-oriented WBS
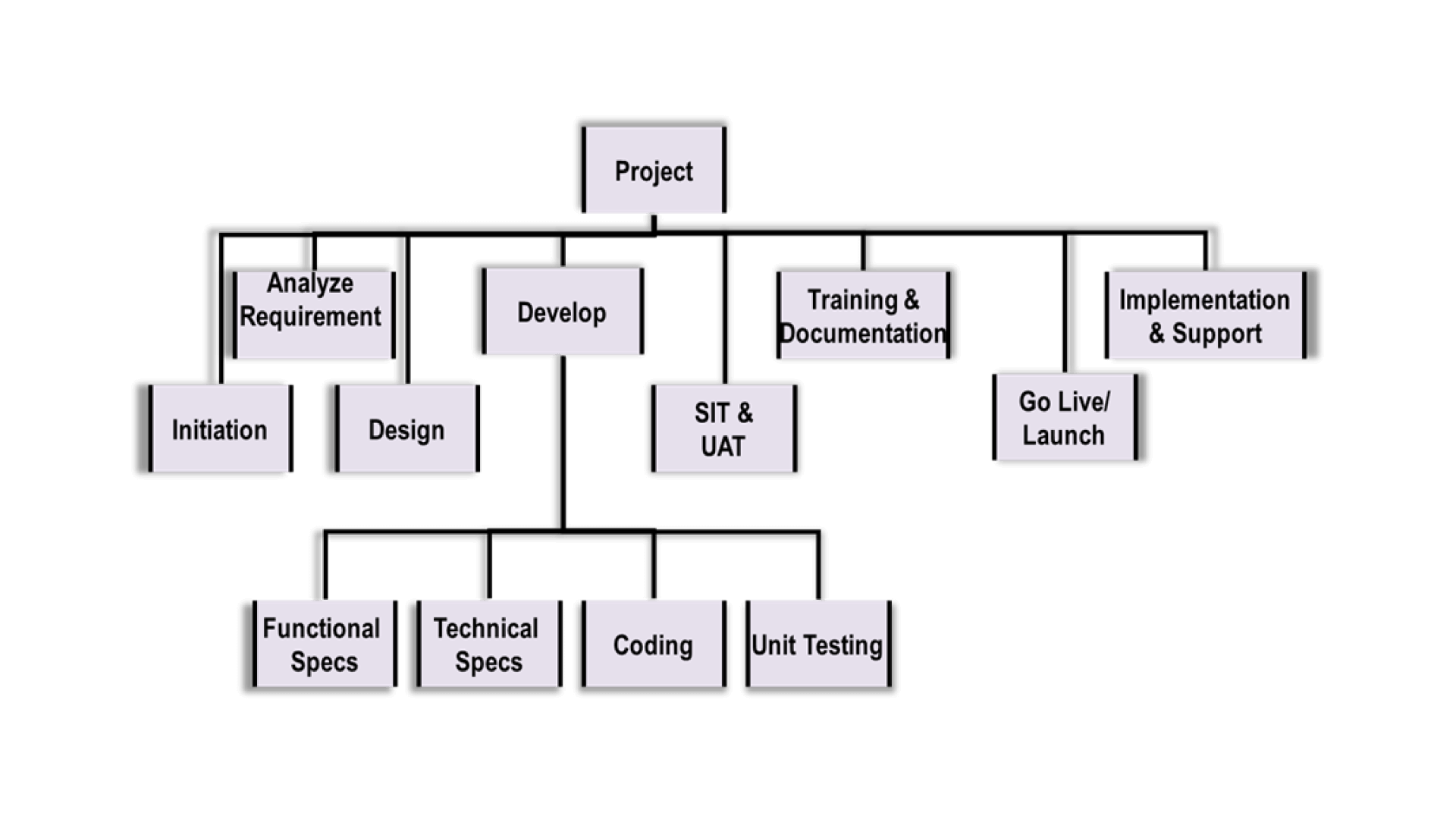
A Noun-oriented WBS (PBS)

Project managers can streamline project workflow by breaking deliverables into work packages, enabling effective task assignment, collaboration, and ownership. Detailed estimation improves planning and scheduling, minimizing delays and cost overruns. The WBS hierarchy allows monitoring and issue identification, facilitating proactive problem-solving. Involving the team fosters engagement and motivation. The WBS serves as a communication tool, ensuring shared understanding among stakeholders. By utilizing decomposition techniques, project managers enhance productivity and increase the chances of project success.

August 9 2023
4 min read

July 18 2023
6 min read

June 19 2023
8 min read

June 12 2023
5 min read